Dijkstra’s Algorithm: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding Shortest Paths in the Real World
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: A Comprehensive Guide to Finding Shortest Paths in the Real World
Introduction: In the field of computer science and networks, we often encounter the challenge of finding the shortest path between two points in a weighted graph. Dijkstra’s algorithm, developed by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956, is a powerful tool for solving such problems. In this article, we will explore in detail how Dijkstra’s algorithm works and its application in the real world.
Understanding Dijkstra’s Algorithm:
Dijkstra’s algorithm solves the shortest path problem in a directed and weighted graph. The goal is to find the optimal route from a source node to all other nodes in the graph. The following are the key steps of the algorithm:
-
Initialization: Assign an initial infinite distance to all nodes, except for the source node, which is assigned an initial distance of 0.
-
Selection of the Nearest Node: Choose the node with the shortest unvisited distance and mark it as “visited”.
-
Updating Distances: Update the distances of all nodes adjacent to the selected node in the previous step. If the current distance is less than the previously stored distance, update it with the new distance.
-
Iteration: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until all nodes are visited or the destination node is reached.
-
Recovering the Shortest Path: Once the algorithm finishes, the shortest path from the source node to any other node can be recovered by tracking the distances and connections stored during the execution.
Real-World Applications:
Dijkstra’s algorithm has a wide range of applications in the real world, especially in fields such as route planning, navigation, and network optimization. Some notable examples include:
-
Packet Routing in Computer Networks: Dijkstra’s algorithm is used to find the shortest routes between routers in a network, enabling efficient routing of data packets.
-
GPS Navigation Systems: Dijkstra-based algorithms are employed to calculate the shortest routes between locations in navigation applications, such as finding the optimal route to reach a destination in the least amount of time.
-
Transportation Networks: Logistics and transportation companies use Dijkstra’s algorithm to optimize delivery routes, minimizing the distance traveled or time required to deliver goods.
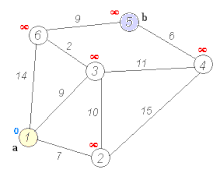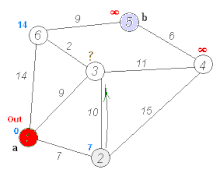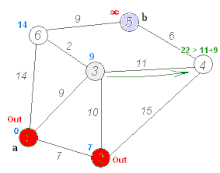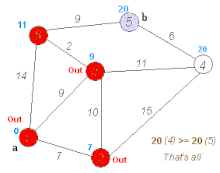
Below is a visual representation of Dijkstra’s algorithm taken from Wikipedia to help understand its operation:
Python Implementation:
Here is an example implementation of Dijkstra’s algorithm in Python:
import heapq
def dijkstra(graph, start):
distances = {node: float('inf') for node in graph}
distances[start] = 0
queue = [(0, start)]
while queue:
current_distance, current_node = heapq.heappop(queue)
if current_distance > distances[current_node]:
continue
for neighbor, weight in graph[current_node].items():
distance = current_distance + weight
if distance < distances[neighbor]:
distances[neighbor] = distance
heapq.heappush(queue, (distance, neighbor))
return distances
Conclusion:
Dijkstra’s algorithm is a fundamental tool for finding the shortest paths in a weighted graph. Its real-world applications span various fields, from packet routing in computer networks to optimizing transportation routes. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with a clear understanding of Dijkstra’s algorithm and its significance in solving real-world problems. Now, you can apply this knowledge to your own projects and challenges!


Comments